How to Use Django's Flatpages App
Django comes with a Flatpages application that enables the user to create flat HTML pages and store it in the database. It can be very usefull for pages like About, Privacy Policy, Cookies Policy and so on.
What exactly is flatpages?
A static web page (sometimes called a flat page or a stationary page) is a web page that is delivered to the user’s web browser exactly as stored, in contrast to dynamic web pages which are generated by a web application.
How it’s actually works?
Basically, we defines a master page for the content to be displayed, then user creates a new flatpage in the Django Admin interface, picks a URL and add the content. The user can also select if the page requires login or not.
Installation
First add the sites and flatpages contrib apps to the INSTALLED_APPS:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
# New apps
'django.contrib.sites',
'django.contrib.flatpages',
]
If you wasn’t using the sites app, you may also need to add a SITE_ID to the settings.py file:
SITE_ID = 1
Now update urls.py with the flatpages urls:
from django.urls import path, include
from django.contrib import admin
urlpatterns = [
path('pages/', include('django.contrib.flatpages.urls')),
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
]
Migrate the databse:
$ python manage.py migrate
Operations to perform:
Apply all migrations: admin, auth, contenttypes, core, flatpages, sessions, sites
Running migrations:
Applying sites.0001_initial... OK
Applying flatpages.0001_initial... OK
Applying sites.0002_alter_domain_unique... OK
Template
- Configure the templates inside
setting.py
TEMPLATES_PATH = BASE_DIR / 'templates' ## Templates path
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [TEMPLATES_PATH,], # Add the templates path here...
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
...
},
},
]
- Create
templatesfolder inside the root of the project wheremanage.pyfile exists. - Create
flatpagesfolder inside the templates folder. - Add a default template for the flatpages. The default location is
flatpages/default.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>{{ flatpage.title }}</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<nav class="navbar navbar-default">
<div class="container">
<div class="navbar-header">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Flatpages</a>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
<h1>{{ flatpage.title }}</h1>
<div class="container">
{{ flatpage.content }}
</div>
</body>
</html>
The important part here is this two variables: flatpage.title and flatpage.content.
Usage
Go to the Django Admin. It will be automatically added to the Django Admin interface.

Now add a new flat page.

Save it and go to the flatpage URL, that is /pages/privacy/:
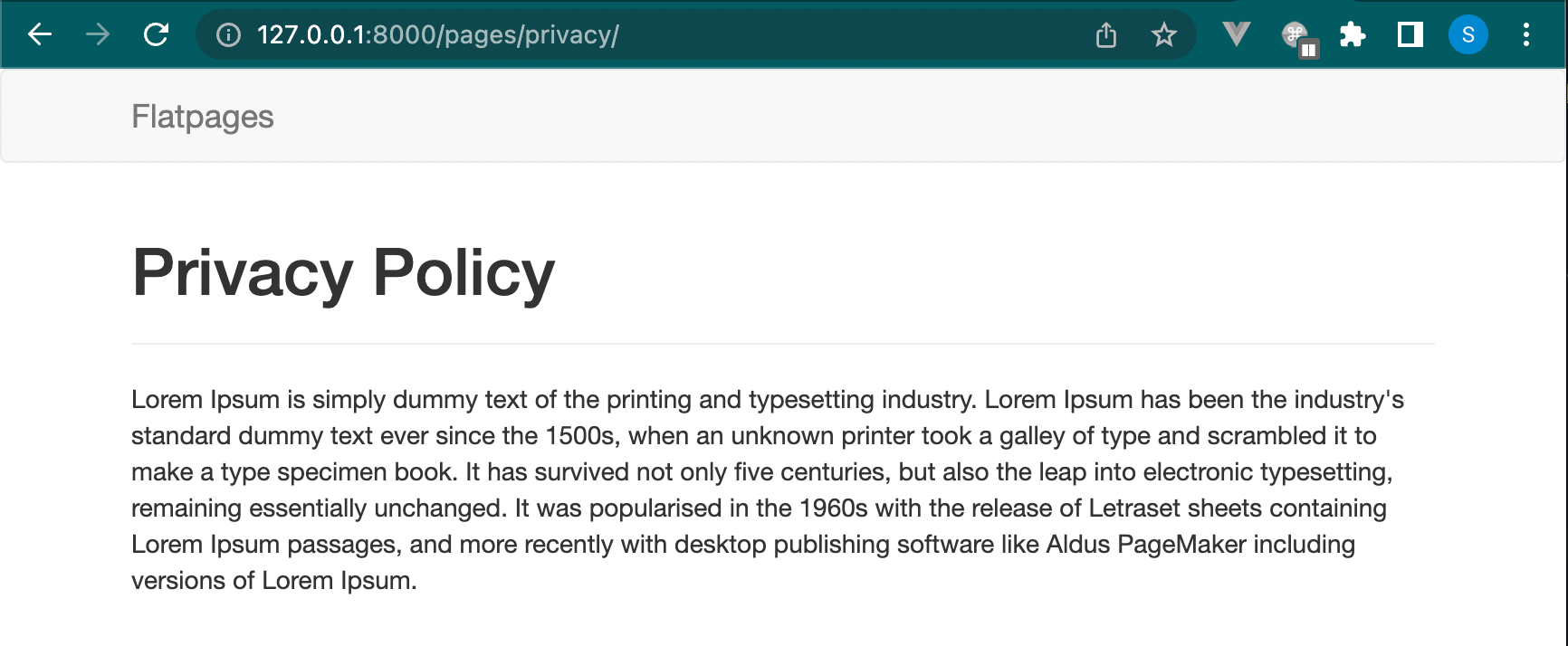
Rendering a List of Flatpages
You can list all the available flatpages like this in a template:
Load the flatpages template tag.
After loading the library, you can retrieve all current flatpages via the get_flatpages tag.
{% load flatpages %}
{% get_flatpages as flatpages %}
<ul>
{% for page in flatpages %}
<li><a href="{{ page.url }}">{{ page.title }}</a></li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
Add the pages into the template snippet:
{% load flatpages %}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>{{ flatpage.title }}</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<nav class="navbar navbar-default">
<div class="container">
<div class="navbar-header">
<button type="button" class="navbar-toggle collapsed" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#menu" aria-expanded="false">
<span class="sr-only">Toggle navigation</span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Flatpages</a>
</div>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="menu">
{% get_flatpages as flatpages %}
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
{% for page in flatpages %}
<li><a href="/pages{{ page.url }}">{{ page.title }}</a></li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
<h1>{{ flatpage.title }}</h1>
<div class="container">
{{ flatpage.content }}
</div>
</body>
</html>
It will look something like that:
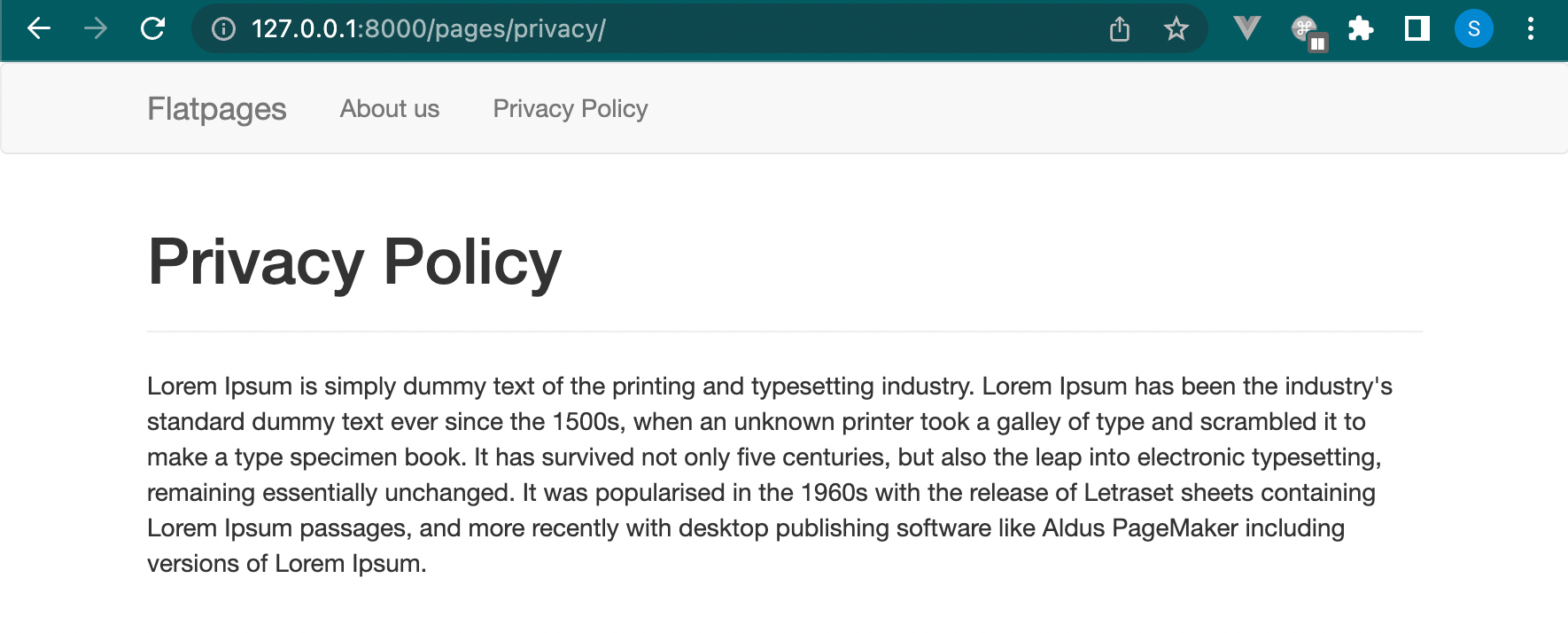
When you click on About us link, It will redirect to the about us page.

If you want to find out more about the Flatpages app, refer to the Django’s Official documentation about it.